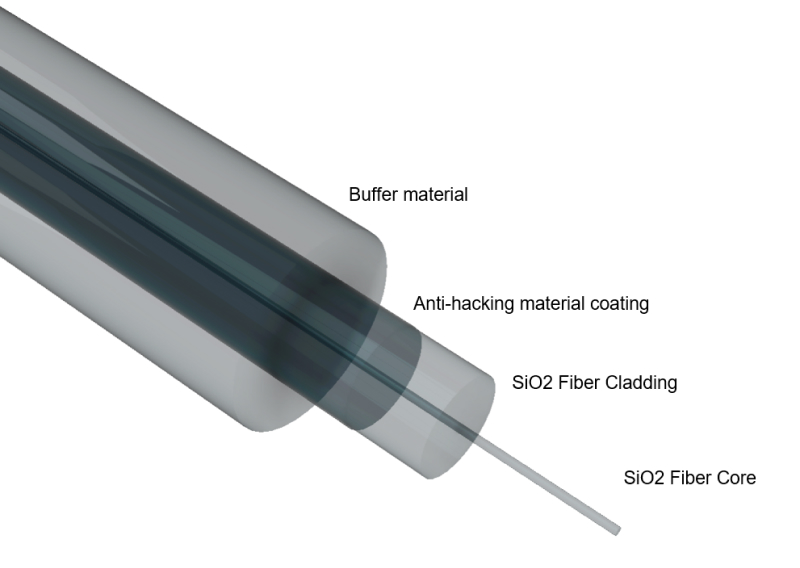
- Key Features and Operating Principles
- Key Application Areas
- Advantages
- Technical Limitations
-
01
Physical Security
Fiber optics, by nature, are difficult to tap or intercept because they are immune to electromagnetic interference and do not emit electromagnetic signals. However, any physical attempt to cut or tap into the cable causes signal distortion or loss. Anti-hacking fiber optic cables are designed to be even more sensitive to such physical tampering attempts, immediately sending alerts or cutting the connection if an intrusion is detected.
-
02
Real-Time Monitoring
Distributed Acoustic Sensing (DAS) technology can be integrated into the structure of these fiber optic cables. This allows the detection of vibrations or physical changes along the fiber in real time. As a result, any attempt to physically manipulate or hack the cable can be instantly identified and responded to.
-
03
Detection and Alert Systems
Anti-hacking fiber optics include systems that detect intrusion attempts, such as cutting, bending, or connector damage, and send real-time alerts. These systems can notify a management system immediately when physical tampering or signal interference is detected.
-
04
High Security
Compared to copper cables, fiber optics are extremely difficult to tap or intercept. To eavesdrop on light signals, physical access to the fiber is necessary, and any such attempt would cause signal distortion or interruptions, making it easily detectable. This makes anti-hacking fiber optics particularly advantageous for the secure transmission of sensitive data.
-
01
Government and Military Organizations
Fiber optics are used to protect state secrets, and enhanced security cables play an even more critical role in these settings.
-
02
Finance and Data Centers
Large data centers and financial institutions use fiber optic networks to reduce the risk of hacking and eavesdropping.
-
03
Industrial Infrastructure
Critical infrastructure, such as energy, telecommunications, and transportation, is protected using anti-hacking fiber optic technology.
-
01
Reliability
Physical hacking or eavesdropping attempts are easily detectable.
-
02
Security
Light signals are immune to electromagnetic interference.
-
03
Real-Time Detection
Technologies like DAS enable real-time detection of physical changes or intrusion attempts.
-
01
Installation Cost
Anti-hacking fiber optic cables are more expensive than standard fiber optic cables, with higher installation and maintenance costs.
-
02
Complexity
The additional systems and technologies required for enhanced security make installation and operation more complex.
